Component Reference
The main strength of Wren:IDM is the simplicity of its core concepts, which is also a cornerstone of its outstanding flexibility. It provides a JSON-based object model, where objects are treated uniformly using APIs. These objects include
-
managed objects – maintained in the IDM repository,
-
system objects – representing external resources such as accounts,
-
configuration objects – representing various aspects of the IDM configuration,
-
workflow objects – representing workflows, and many more.
Working with these objects is pretty straightforward as well. For example, when you patch a managed object such as a user, it is updated in the repository and configured actions take place. When you patch a system object such as an account, it is updated in the integrated system. In both cases audit trails are recorded in the system.
The main system components are shown in following figure:
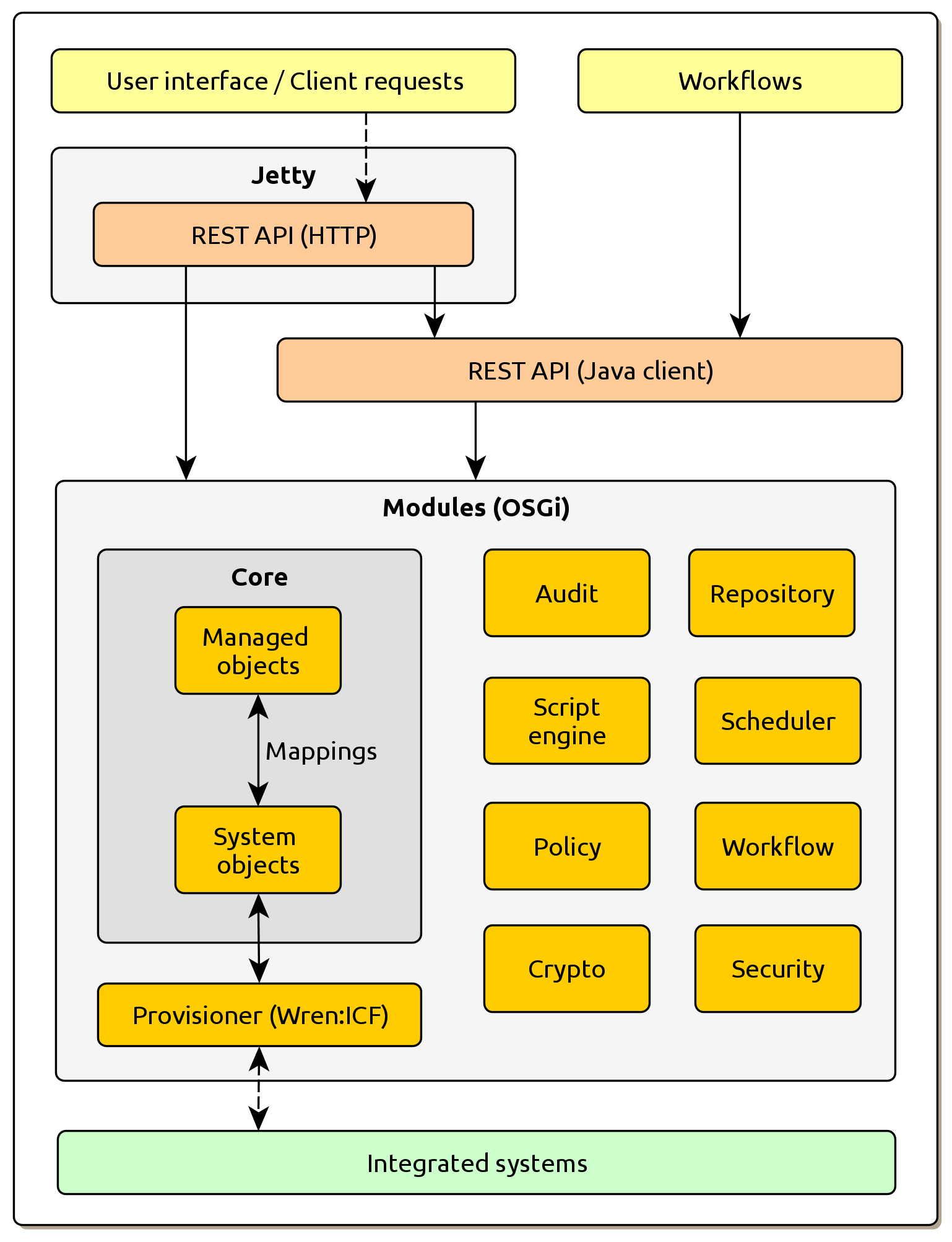
While the depicted components are quite familiar, Wren:IDM takes a novel approach by providing access to all of them through a unified Resource API. The API is the same whether objects are being accessed through REST from outside the system, or internally from scripts and other parts of the IDM system itself. Please compare the following two examples.
// JavaScript Resource API within IDM
var users = openidm.query("managed/user", { "_queryFilter" : '/givenName eq "Peggy"' });$ # REST API accessed from outside. Never use plain HTTP over network.
$ # Also consider mutual certificate authentication for similar use cases.
$ curl -u openidm-admin:openidm-admin \
'http://localhost:8080/openidm/managed/user?_queryFilter=givenName+eq+"Peggy"'As already stated, the components are familiar from most IDM platforms:
-
Audit – auditing of all triggered events and states
-
Crypto – component responsible for data encryption
-
Custom endpoints (not shown in the diagram) – REST API endpoints defined by the implementers with their own business logic
-
Managed objects – IDM managed objects such as users, roles or any objects the organization uses
-
Policy – executing validations during object modifications
-
Repository – persistence layer for storing all managed objects
-
Scheduler – scheduled job management and execution
-
Script engine – component for scripts execution (JavaScript or Groovy)
-
Provisioner – abstract layer for integrating external systems
-
Security – REST API security
-
System objects – integrated system objects (exposed via provisioners)
-
Workflow – embedded workflow engine based on Flowable framework